Tasks
Introduction
In your BPMN process, it is the Task objects that actually do the work! Typically, you will start modeling a business process using standard tasks, but then as you develop your model into an executable business process, you will change these to more specific task types that, for example, call APEX pages, run scripts, and send messages. This section describes those tasks and how to use and configure them.
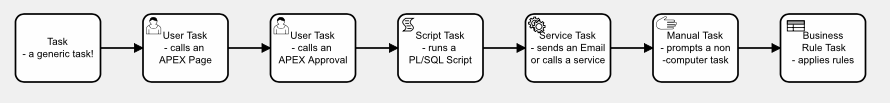
Supported Task Types
1. bpmn:task - Task
This is the standard, generic, BPMN task. It has no special behavior when a process is executed.
Typically these are used in the early stages of modeling a business process, but as a project moves towards creating an executable process model, you will convert standard tasks to one of the more specific task types listed below.
2. bpmn:userTask - Calls an APEX Page or an APEX Approval Task
userTask objects can be used for an online task to be performed by a user. Currently, the following userTask types are enabled:
- call an APEX page
- call an APEX Human Task (an APEX Approval Task or Action Task)
- call a Flows for APEX Simple Form
The userTask type and all of the task settings are configured in the modeler properties panel. For information on how to define all of the settings for user tasks, see here.
3. bpmn:scriptTask - Runs a PL/SQL script
scriptTask runs a user supplied PL/SQL function. Good practice would be to have this call an existing procedure or package, which implements your application logic.
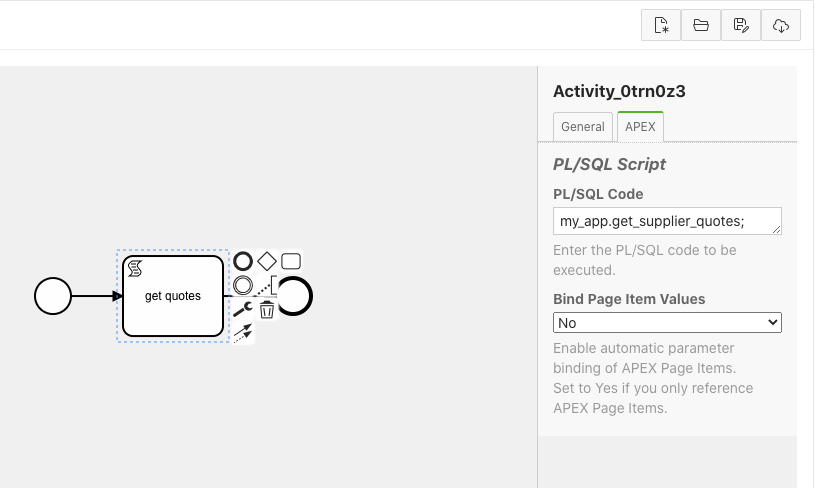
Process variables and pseudo variables are available inside your PL/SQL procedure as follows:
- Flows for APEX Process Variables. Process variables can be retrieved and used inside your procedure, using the flow_process_vars setters and getters.
-
Flows for APEX Pseudo Variables. Process ID, Subflow ID, and Step Key are available inside your procedure using following function calls
flow_globals.process_id flow_globals.subflow_id flow_globals.step_key
In earlier versions of Flows for APEX, prior to v21.1, you could have done this using the syntax flow_plsql_runner_pkg.g_current_prcs_id, which is now deprecated.
For example, where we have a process variable ordr_id that is used to link our business process to its subject order, we can retrieve the order ID inside our procedure using the following code snippet:
l_process_id := flow_globals.process_id;
l_order_id := flow_process_vars.get_var_vc2
( pi_prcs_id => l_process_id,
pi_var_name => 'ordr_id' );
APEX Page Item values are available to your procedure if you opt to bind them into your process in the modeler. By default, they are not available. Furthermore, using Page Items to pass values from one process step to another is not recommended, and from V22.1 is now deprecated. Instead, you should use Process Variables to pass values from one process step to another.
Note that, depending upon your process, a scriptTask might not be executed from the context of an APEX page, and so APEX Page Items might not be available. This would occur if a script is run (or re-run) later, after another user has performed part of the process, or if a task operates as a result of, for example, a timer firing. Use of Page Items to pass values between steps also makes your process steps non-restartable in the event of an error. For all these reasons, you should use Flows for APEX process variables as a variable system that is persistent for the life of your business process, rather than APEX page variables which only persist during a user session.
4. bpmn:serviceTask - for running external services
Currently serviceTask can be used for the following services:
- Sending Mail defined declaratively in your process model. 🆕
- Sending Mail using an APEX_MAIL template. 🆕
- Running a PL/SQL script to run your own serviceTask.
5. bpmn:manualTasks - for non-IT tasks
manualTasks do not currently have any special functionality and currently behave like a standard bpmn:task objects.
6. bpmn:businessRuleTask - for automated decision making🆕
Currently businessRuleTask can be used for the following services:
- Running a PL/SQL script to run your own businessRuleTask, including to call AI / ML services inside your Oracle database.🆕
7. bpmn:sendTask - for sending a message to another process instance🆕
The sendTask is used for sending a message to another process using BPMN messageFlow. These messages can be used to start, stop, or synchronize process steps across processes, and can also be used to send information as a payload to another process.
Flows for APEX messageFlow uses a standard message format to communicate between processes, which is described in detail here. Messages can be sent with sendTasks or Message Throw Events, and can be received or caught by receiveTasks or Message Catch Events, interchangeably.
If you decide not to use the declarative Basic APEX Message format that is built into these activity and event types, you can use sendTask to run your own PL/SQL script to send a message - but this is only supported on SendTask (not receiveTask or the throw and catch message events).
8. bpmn:receiveTask - for receiving a message from another process instance.🆕
A receiveTask is configured to wait to receive a Basic APEX Message formatted messageFlow, and then on receipt, progress a workflow. Optionally, a message payload can be included to send information between the processes. More information about MessageFlow, see here.