Pool and Lanes
Introduction
BPMN provides features to model who is performing activities and tasks in a modeled business process.
Current Support
Flows for APEX supports a process running in a pool of 1 or more lanes. Within a pool, process progression occurs using sequence flows. A well-formed BPMN diagram will contain named lanes showing who performs the process activities.
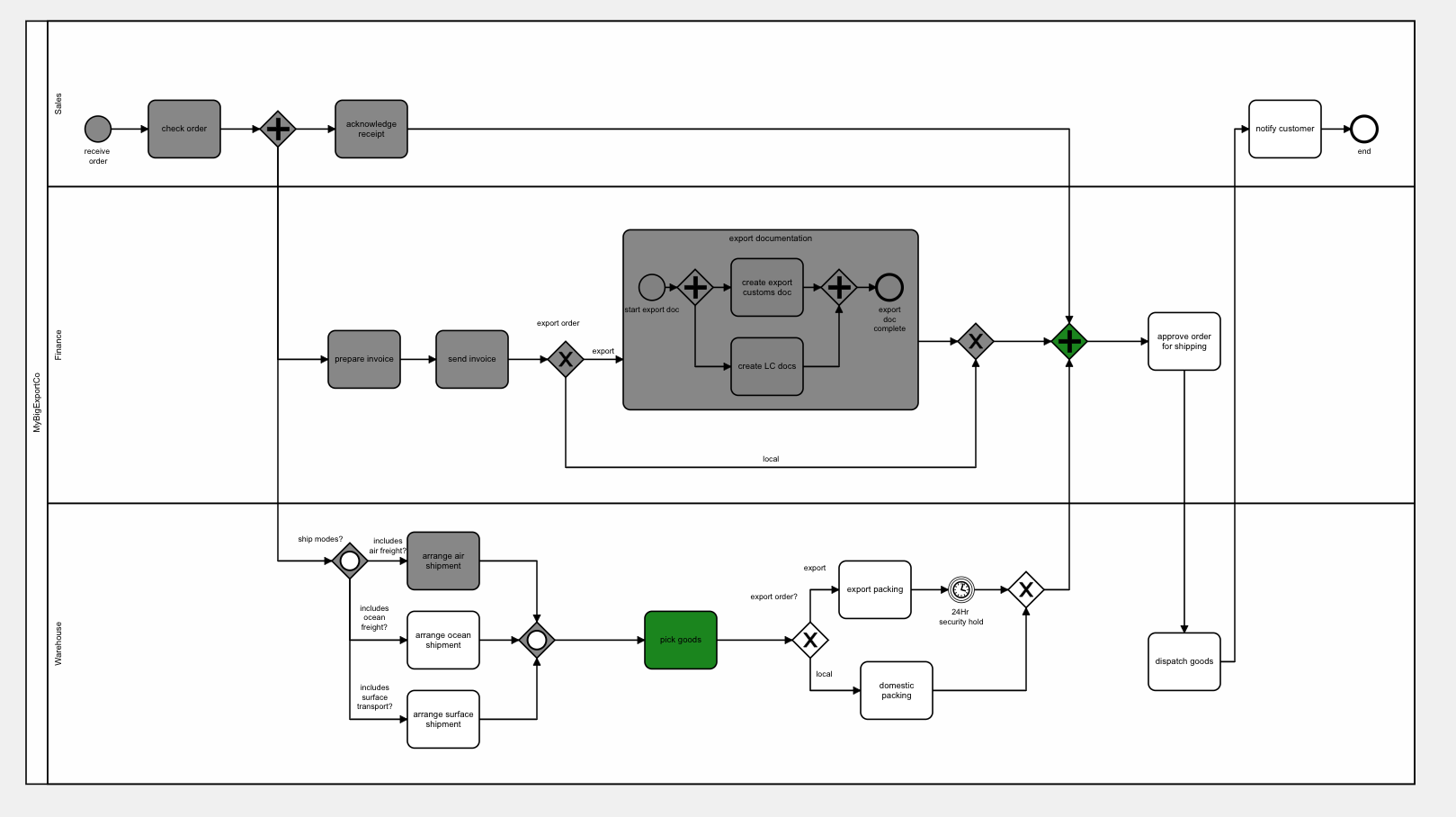
In this example, the process occurs in one pool (“MyBigExportCo”), and has three process lanes - Sales, Finance, and Shipping.
When this example is run, the lane information of the current tasks on each running subflow are available to the application, and could be used to make next task inboxes for users servicing that pool.
Cross Pool Processes
Processes which are defined with multiple pools use message flows and signal flows to define communication between process objects in different pools, rather than sequence flows which are used inside a pool.
Flows for APEX does not currently support processes using message flows and signal flows, and so multi-pool diagrams cannot currently be run.
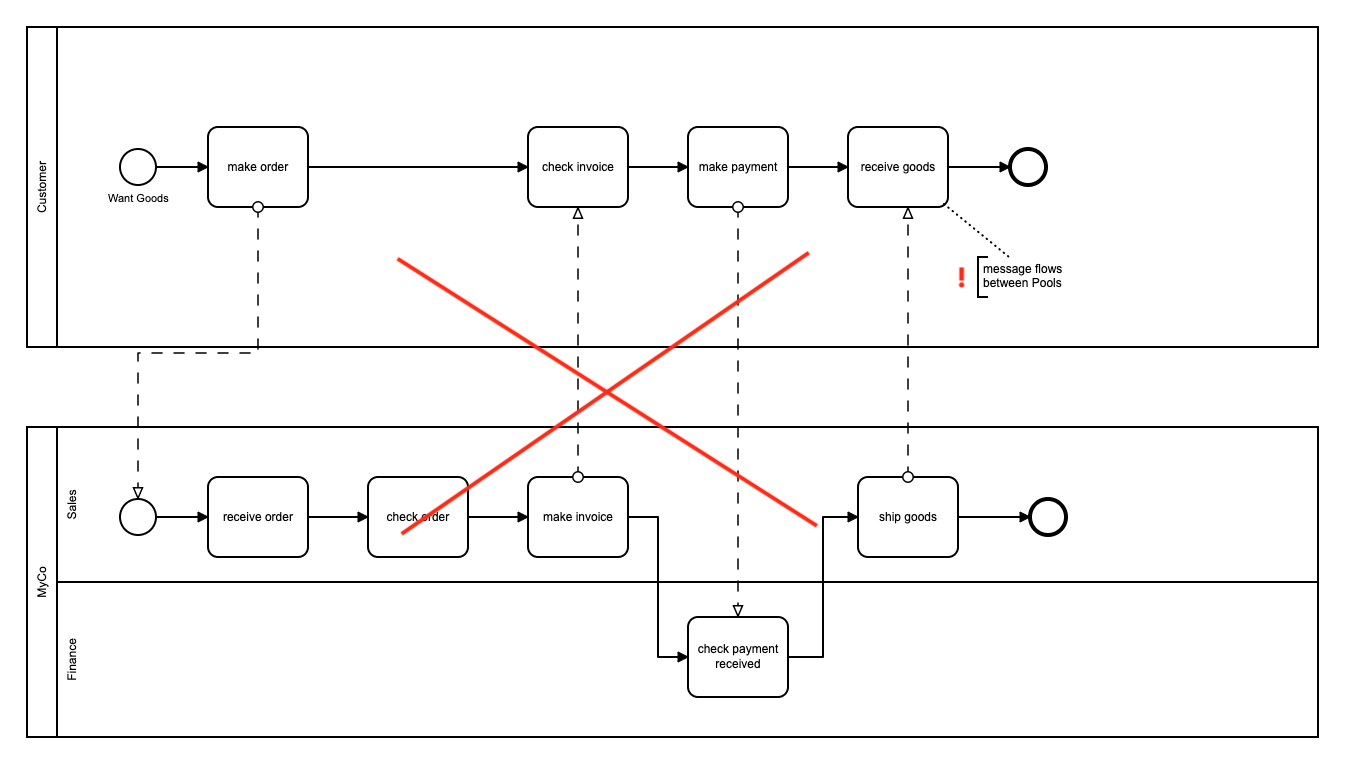 This example models (correctly, in BPMN terms!) the customer and company in separate pools. However, Flows for APEX cannot currently handle messageflow across pool boundaries. sequenceFlow has to be contained inside a pool.
This example models (correctly, in BPMN terms!) the customer and company in separate pools. However, Flows for APEX cannot currently handle messageflow across pool boundaries. sequenceFlow has to be contained inside a pool.
Multi User Pools and Task Reservation
If you are using Flows for APEX for task orchestration or have an application where users are provided with a task inbox, all users who are serving a lane will see all of the current tasks in that lane. Task Reservation provides a mechanism for users who are sharing a lane to record that they are working on a task , or intend to work on a task, so that other users don’t also work on the same task.
Tasks can be reserved, by calling the flow_api_pkg.flow_reserve_step procedure. When you reserve a step, you supply a reservation as the p_reservation argument. This would usually be set to the username of the user making the reservation - although an application might want to have some other scheme for reservation value.
A task reservation can also be explicitly released by calling flow_api_pkg.flow_release_step procedure.
Reservation only applies to the current step on a subflow, and is implicitly released when the step is completed and the process continues to the next step, i.e., when flow_api_pkg.flow_complete_step is called.
The Flows For APEX Task Reservation is a light weight mechanism to signal to others that this task is reserved and will be worked on by the reserving user. Out of the box, IT IS NOT A SECURITY MECHANISM to prevent unauthorized users from working on a task. YOU SHOUD NOT RELY ON THIS MECHANISM TO CONTROL TASK AUTHORIZATION OR OTHER ACCESS CONTROL OBJECTIVES.
As part of your application design, you might want to wrap these procedures with your own application-specific controls to implement control on who can reserve (and for whom), and who can release reservations.